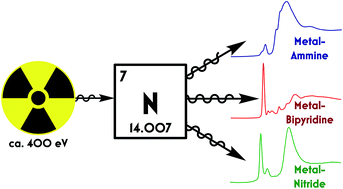
An energydispersive (ED) Xray computed tomography (CT) system is useful for carrying out monochromatic imaging To perform enhanced iodine Kedge CT, we developed an oscillation linear cadmium telluride (CdTe) detector with a scan velocity of 25 mm/s and an energy resolution of 12 keVCT is performed by repeated linear scans and rotations of an objectSodium tungsten 3 trioxide is composed of regular ReO octahedra bronze Na WO was used for comparison 6 06 3 (R(Re—O)"1875 As ) joined by vertices with the A places Xray absorption experiments at the O Kedge were being vacant tris(dithiolene) complexes of tungsten Here, we derive the estimated branching ratio (EBR), defined as the relative intensity of the L 3edge over the sum of the L 3 and L 2edges, I(L 3)/ 3 L 2), 23−26 and the L 1 risingedge energy for each reference compound These two metrics are used to gauge whether the level of detail provided

Ct Image Contrast Of High Z Elements Phantom Imaging Studies And Clinical Implications Radiology
K edge of tungsten
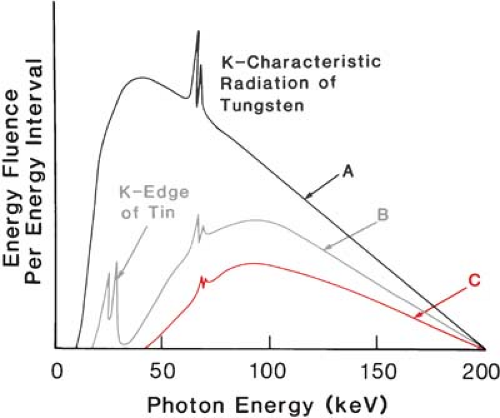
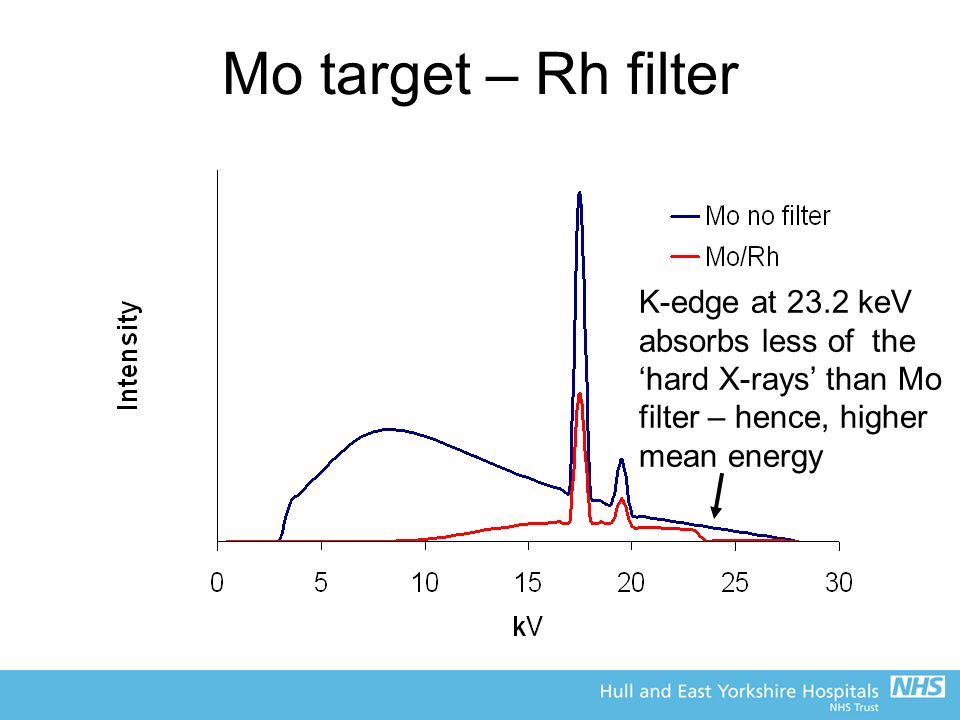
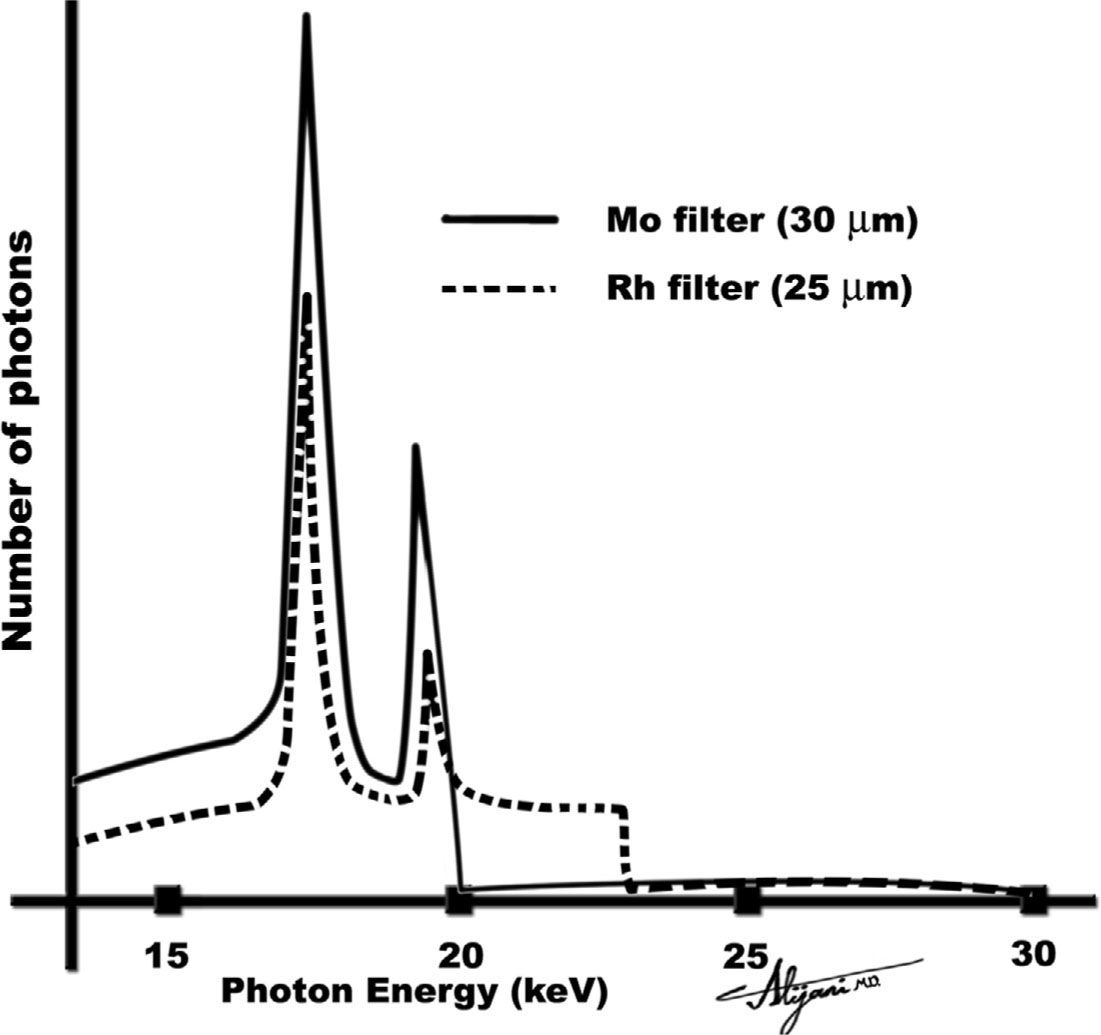
K edge of tungsten-Rhodium has a kedge at 233 keV and we can use a molybdenum target and rhodium filter (MoRh) to increase the amount of xrays with energies in the range of 233 keV Rhodium characteristic xrays are at 2 227 keV When used as a target this produces a beam with a mean energy that is higher than for MoMo and for MoRh This range does not correspond to the Kedge of iodine but to that of tungsten, the major component of the xray tube anode of CT scanners At such energy, radiolysis of the ICM produces sodium or potassium iodide that prevents a normal DNA breaks repair and influences the individual response to xray lowdose



The Physics And Technology Of Mammography
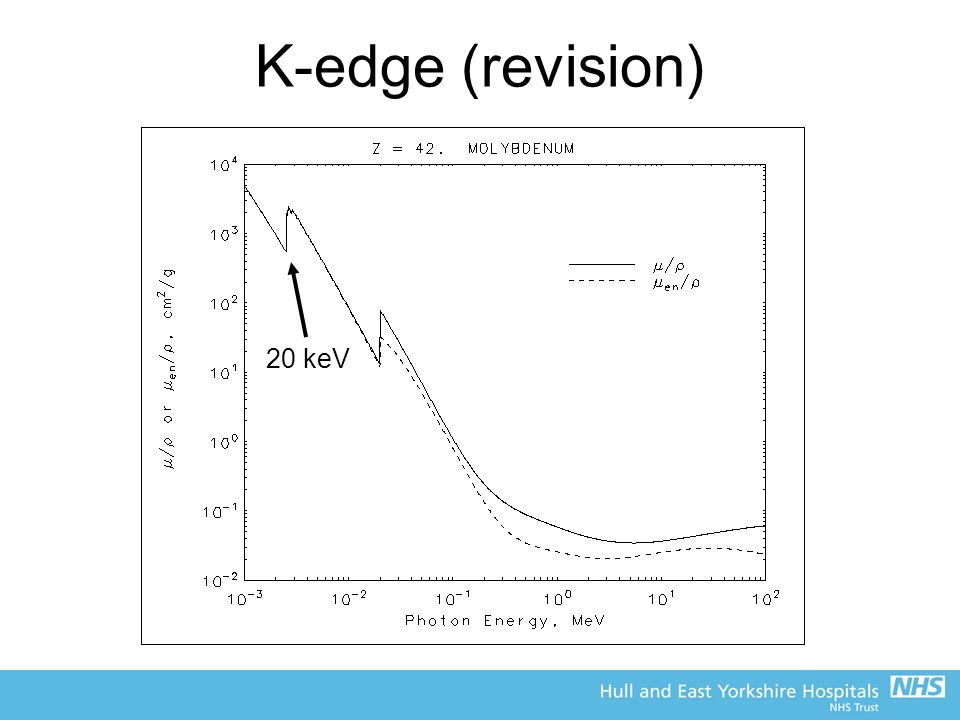
The kedge is the minimum energy required for the photoelectric event to occur with a kshell electron below this level, no photoelectric events can occur with k electrons Kshell electrons are important because the energy to dislodge them (produce photoelecric absorption) is right in the middle of the diagnostic range The energy fluence of the K lines of tungsten can be preferentially reduced using a tin filter Because the K absorption edge of tin is at about 292 keV (), it strongly absorbs photons above 292 keV by the photoelectric processHowever, lowerenergy photons cannot eject the K The design of the instrument is based on the proven 'Hybrid instrument configuration', 3, 10, 11 which incorporates both techniques of Kedge densitometer (KED) and Xray fluorescence analysis (XRF) of Kseries XraysThe main objective of developing this HKED facility is to assay the spent reprocessing solutions received from CORAL and
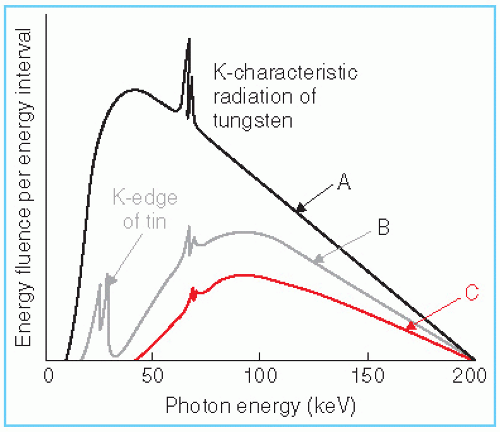
For the work described here, tungsten, with a kedge energy of 695 keV, Footnote 1 was thus selected as an element of choice for Xray CA Fig 1 The mass attenuation coefficient for iodine and tungsten superimposed with a typical 1 kV CT Xray spectrum Full size imageThe Kedge energy is, in turn, determined by the atomic number of the material Calcium tungstate, the most common screen material for many years, uses tungsten as the absorbing element The K edge of tungsten is at 694 keV For most xray examinations, a major portion of the xray beam spectrum falls below this energyAbstract Synchrotron radiation microXray fluorescence (SRμXRF) is a powerful elemental mapping technique that has been used to map tungsten and zinc distribution in bone tissue However, the heterogeneity of the bone samples along with overlap of the tungsten Ledge with the zinc Kedge signals complicates SRμXRF data analysis, introduces minor artefacts into the
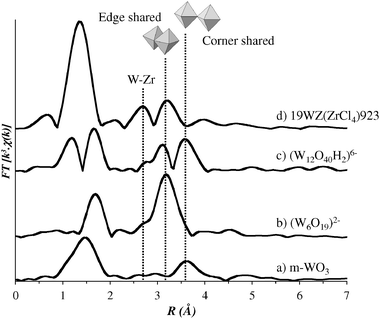
Band which will contain the tungsten Ka lines, and, because of the slight difference in the shape of the two transmission curves, the subtracted spectrum is expected to be negative just below the Er K edge (575 keV) The unscattered primary spectra measured with the Er and Yb filters are shown inTungsten 3695 K (3422 °C, 6192 °F) 63 K (5930 °C, °F) 193 g/cm3 5231 kJ/mol34 2427 J/(mol·K) 528 nΩ·m (at °C paramagnetic5 Molybdenum 26 K (2623 °C, 4753 °F) 4912 K (4639 °C, °F) 1028 g/cm3 3748 kJ/mol 2406 J/(mol·K) 534 nΩ·m (at °C) paramagnetic4 TitaniumAbstract and Figures The local structure of tungsten species in tungsten–zirconium–oxide catalysts (WOxZrO2) was first investigated by W Kedge xray absorption spectroscopic techniques A




Oxygen K Edge X Ray Absorption Spectra In Pure Oxides Reo And Wo Download Scientific Diagram




K Edge Angiography Utilizing A Tungsten Plasma X Ray Generator In Conjunction With Gadolinium Based Contrast Media Sciencedirect
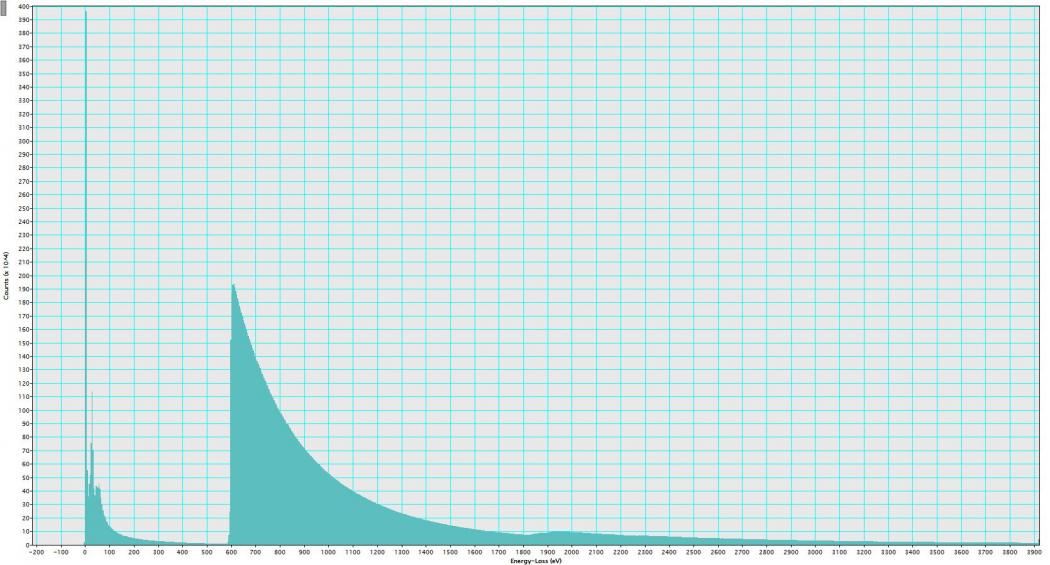
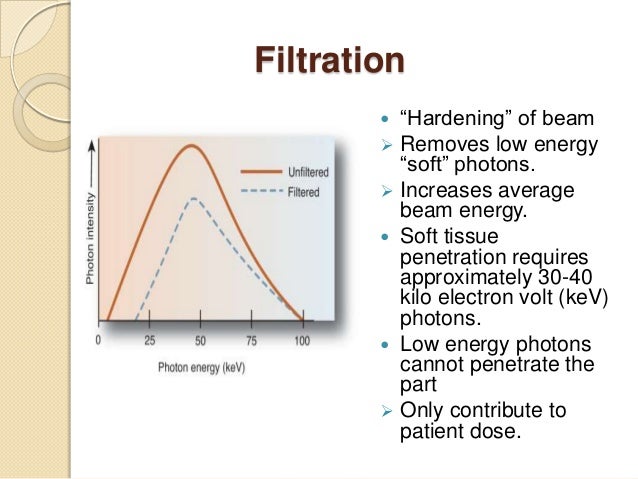
The Kedge of an element is the energy level at which Xray photons have just enough energy to knock out atomic electrons on the Korbit and a substantial increase in Xray absorption results Mo, Rh, and Ag are typical elements with suitable Kedge energies for providing added beam filtration for mammography ( Figure 43 ) This xray transition table provides the energies for K transitions connecting the K shell ( n = 1) to the shells with principal quantum numbers n = 2 to 4 and L transitions connecting the L 1, L 2, and L 3 shells ( n = 2) to the shells with principal quantum numbers n = 3 and 4 The elements covered include Z = 10, neon to Z = 100, fermium The EELS spectra in Figure 6 acquired from the tungstenencrusted cell surface layer, showed the presence of a carbon Kedge at 284 eV, which is similar to the carbon Kedge of a tungsten carbide (WC) reference in terms of both edge energy position and



Tungsten Eels Info



Mp 91 W Cubic Im 3m 229
The kedge represents the energy needed to eject a Kshell electron (the innermost and most strongly bound electrons) Outer shell electrons have absorption edges but these are much too low energy to be relevant In soft tissues, the dominant elements (eg C, H, O, and N) have very low Kedges, in the range of a few keVExtended Xray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and S Kedge absorption studies of the amorphous tungsten sulfide, WS, and EXAFS studies of the amorphous tungsten selenide, WSe, suggest these compounds can be formulated as W(S) and W(Se) The observed metal–metal distances of 275 Å are consistent with the formatThe KEdge in the photon attenuation of tungsten can be noticed as a drop of the continuum at the binding energy of 695 keV For tungsten targets the fraction of Kradiation contributing to the total energy fluence is




High Energy X Ray Backlighter Spectrum Measurements Using Calibrated Image Plates Review Of Scientific Instruments Vol No 2




File X Ray Spectra With And Without Filtration Jpg Wikimedia Commons
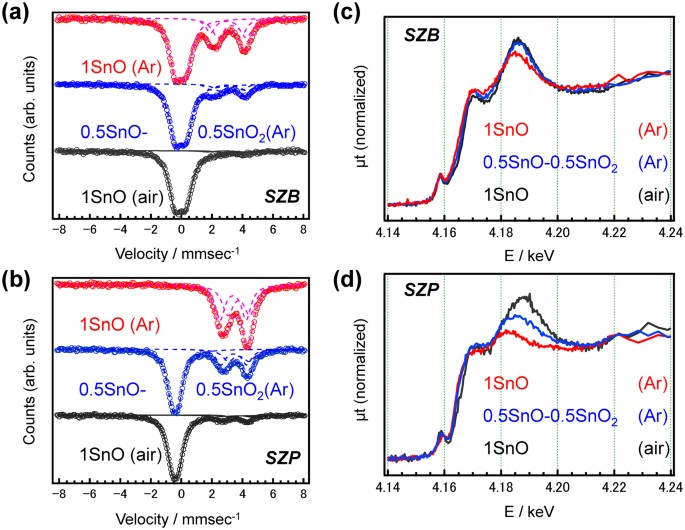
The local structure of tungsten species in tungsten–zirconium–oxide catalysts (WO x ZrO 2) was first investigated by W K‐edge x‐ray absorption spectroscopic techniques A proportion of WO 4 to the total WO x species was quantitatively analyzed with W L 1 ‐edge x‐ray absorption near edge structure (XANES)Molybdenum or tungstencontaining enzymes catalyze oxygen atom transfer reactions involved in carbon, sulfur, or nitrogen metabolism It has been observed that reduction potentials and oxygen atom transfer rates are different for W relative to Mo enzymes and the isostructural Mo/W complexes Sulfur Kedge Xray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and density functional theory Eiichi Sato, Etsuro Tanaka, Hidezo Mori, Hiroki Kawakami, Toshiaki Kawai, Takashi Inoue, Akira Ogawa, Mitsuru Izumisawa, Kiyomi Takahashi, Shigehiro Sato, and Kazuyoshi Takayama "Kedge magnification digital angiography using a 100umfocus tungsten tube," Optical Engineering 46(2), (1 February 07)



Http Cais Uga Edu Wp Content Uploads 19 01 Xrf Background Pdf




Pdf X Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study At The Si K Edge Of Tungsten Carbide Silicon Carbide Thin Films Semantic Scholar
Tungsten anode xray tubes and aluminum filtration, the standard for all other types of radiography, is not The kedge energy is equivalent to the binding energy of the kshell electrons which is determined by the size (atomic number, Z) of the atom In principle, a filter material can be selected to position the kedge and filter cutoff The average photon energy of the tungsten K α lines is shown above the gadolinium Kedge The average photon energy is 5 keV, and gadolinium contrast media with a Kabsorption edge of 502 keV absorb the lines easily Therefore, blood vessels were observed with high contrasts Download Download fullsize image; The tungsten–iron–sulfur enzyme acetylene hydratase stands out from its class because it catalyzes a nonredox reaction, the hydration of acetylene to acetaldehyde Sequence comparisons group the protein into the dimethyl sulfoxide reductase family, and it contains a bismolybdopterin guanine dinucleotideligated tungsten atom and a cubanetype 4Fe4S cluster



Condensed Matter Free Full Text Structural Evolution Of Moo3 Thin Films Deposited On Copper Substrates Upon Annealing An X Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study Html



2
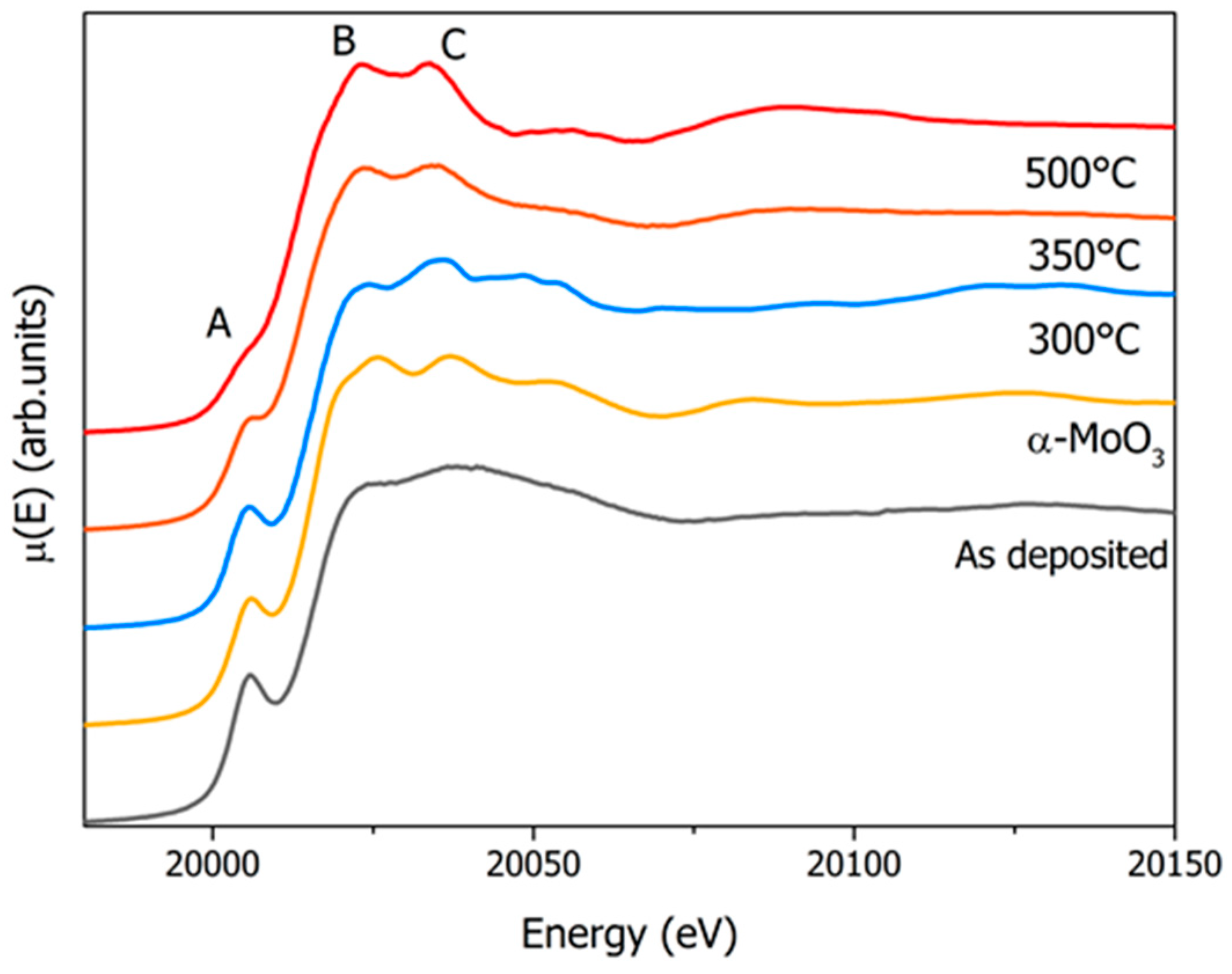
In this work we present an interpretation of experimental O Kedge xray absorption near edge structure (XANES) in perovskitetype WO3 and AWO3 compounds (A = H and Na) using three different first principles approaches (i) fullmultiplescatteringMum value of 050 mA, and the tube voltages for I and GdKedge radiograms were 60 and 80 kV, respectively In the IKedge radiography of a dogheart phantom at an energy range of 33 60 keV, the muscle density increased, and fine coronary arteries were visible Utilizing GdKedgeThe local structure of tungsten species in tungsten–zirconium–oxide catalysts (WOxZrO2) was first investigated by W Kedge xray absorption spectroscopic techniques A proportion of WO4 to the total WOx species was quantitatively analyzed with W L1edge xray absorption near edge structure (XANES) Tungsten species in 15 wt% WOxZrO2, which is the most active for nbutane



Quality Of X Ray Beams Radiology Key



Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf
Abstract A number of authors have calculated the optimum Xray energies for mammography using, as a criterion, the maximum signal to noise ratio (SNR) per unit dose toPhoton energies, in electron volts, of principal K, L, and Mshell emission lines Element K α 1 K α 2 K β 1 L α 1 L α 2 L β 1 L β 2 L γ 1 M α 1 3 Li 543 4 Be 1085 5 B 13 6 C 277 7 N 3924 8 O 5249 9 F 6768 10 Ne 8486 8486Kedge (6) Sports & Outdoors Bike Chains Bike Parts $15 – $25 $25 – $50 $50 – $100 shipping same day delivery include out of stock only eligible items Pickup, delivery & in stores



Escholarship Org Content Qt9rd0c0vg Qt9rd0c0vg Nosplash 181d121fdd5a8fffeea5b6e Pdf



Section 4
The suitability of such spectra for practical use has been assessed by comparing both the film image quality and the incident breast dose obtained using a Kedge filtered tungsten anode tube with that obtained using a molybdenum anode tube• Cut tungsten electrodes 3/32 to 1/8 diameter by using 2 pairs of pliers and a twisting motion or notched the electrode on the grinding wheel and used two pairs of pliers • Cut tungsten electrodes over 1/8 diameter using a sharp hammer blow to the electrode on a sharp metal edge or notching the electrode on a grinding wheel and striking the In the case of a 100kVp xray machine, barium, with a Kedge of 374 keV, is an excellent absorber When the mean energy increases significantly, tungsten, with a Kedge of 695, becomes a better choice as a radiopaque material COMMON RADIOPACIFIERS Barium Sulfate




X Ray Absorption Spectroscopy




Photon Counting X Ray Imaging With K Edge Filtered X Rays A Simulation Study Atak 16 Medical Physics Wiley Online Library
Kline spectra from tungsten heated by an intense pulsed electron beam For a few atom pairs, the Kedge of one is only a few tens of eV higher than a Kline energy of another, so that a smallSearch for Xray transition energies by element(s), transition(s), and/or energy/wavelength rangeThe Kabsorption edge ( Kedge) refers to the abrupt increase in the photoelectric absorption of xray photons observed at an energy level just beyond the binding energy of the kshell electrons of the absorbing atom Kshell binding energies are specific to each element As the atomic number ( Z) of an element increases, so does its corresponding kshell binding energy, and therefore the greater the photon energy at which the Kedge




A W Anode Spectra With A Low Energy Al Filter B W Anode And A Download Scientific Diagram



Mineralogy Notes 5
According to the XAS result, the shape of the W L 3edge undergoes no considerable changes This infers that structural transformation of tungsten oxide nanoparticle may be caused by the migration of oxygen after sintering From the O Kedge of absorption spectrum, it suggests that a mixture phase structure is obtained when sintered below 300°CMolybdenum Kedge and tungsten L III edge extended Xray absorption fine structure spectroscopic (EXAFS) studies have been carried out on the mixed molybdenum–tungsten compounds Zn 2 Mo 3–x W x O 8 to investigate the metal–metal bonding in these materials and to determine whether there is any tendency to form homo or heterometallic M 3 clusters There is Element Atomic Number Atomic Weight K Edge L1 Edge L2 Edge L3 Edge M1 Edge M5




Isoelectronic Tungsten Doping In Monolayer Mose2 For Carrier Type Modulation Li 16 Advanced Materials Wiley Online Library




Ct Design And Operation Oncology Medical Physics
The Kalpha 1 emission is slightly higher in energy (and, thus, has a lower wavelength) than the Kalpha 2 emission For all elements, the ratio of the intensities of Kalpha 1 and Kalpha 2 is very close to 21 An example of Kalpha lines is Fe Kalpha emitted as iron atoms are spiraling into a black hole at the center of a galaxyUsing the 2meter focusing curved crystal gammaray spectrometer, careful measurements were made of the wavelengths of the K series lines and K absorption edge of tungsten for the dual purpose of establishing a precision linkage between wavelength measurements in the gamma and xray regions and of improving our knowledge of the tungsten wavelengths The highMIV edge, the spinorbit split partner of theMV as well The measurements presented here cover the spectral region continuously from 1606 to 2106 eV Previous measurements of the mass absorption coefficient of tungsten in this spectral region have been limited to the Kaemission lines of Al and Si at 1487 and 1739 eV, respectively12,13 II



Frcr Physics Lectures Diagnostic Radiology Ppt Video Online Download



Eels Measurement Of Aluminum Al
The filament is constructed from a spiral of tungsten wire (melting point 3410 °C), which is set in a nickel block This block supports the filament and is shaped to create an electric field that focuses the electrons into a slit beam The anode has a bevelled edge, which is at a steep angle to the direction of the electron beamWhere this data came from The scattering factor data files indexed through the table above were calculated using the subroutine library by Brennan and Cowan (see references)The values for f' and f" are derived using the theoretical approximation developed by Cromer and Liberman This theory gives accurate values far from an absorption edge but does not account for the effects of



Pubs Acs Org Doi Pdf 10 1021 Acs Chemrev 9b



Quality Of X Ray Beams Radiology Key



Q Tbn And9gcsse64pf0anonw5zbqjwczjqyvpykbctiugz1q9buozb9eswzcw Usqp Cau




Ct Image Contrast Of High Z Elements Phantom Imaging Studies And Clinical Implications Radiology



Osa Towards Poisson Noise Limited Optical Pump Soft X Ray Probe Nexafs Spectroscopy Using A Laser Produced Plasma Source




X Ray Filters




X Ray Imaging Physics For Nuclear Medicine Technologists Part 2 X Ray Interactions And Image Formation Journal Of Nuclear Medicine Technology




The K Absorption Edge Of An Unknown Element Is 0 171 A A Identify The Element B Find The Average Wavelength Of The K Alpha K Alpha K Beta K Gamma Lines C If A 100 E V Electron Strikes The




Xanes Spectra Of 1 Vitreous Samples At The Tungsten L1 Absorption Download Scientific Diagram



Projection Radiography Ii Radiology Key




Oxygen K Edge X Ray Absorption Spectra In Pure Oxides Reo And Wo Download Scientific Diagram



Tungsten Eels Info




Xanes O K Edge Structure Energies Ev For Rhenium And Tungsten Oxides Download Table



Scrutinizing Metal Ligand Covalency And Redox Non Innocence Via Nitrogen K Edge X Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Chemical Science Rsc Publishing



Ieeexplore Ieee Org Iel7 Pdf



Www Physicamedica Com Article S11 1797 18 4 Pdf




Full Field Fan Beam X Ray Fluorescence Computed Tomography System Design With Linear Array Detectors And Pinhole Collimation A Rapid Monte Carlo Study




Sulfur K Edge Xas Of Wvo Vs Movo Bis Dithiolene Complexes Contributions Of Relativistic Effects To Electronic Structure And Reactivity Of Tungsten Enzymes Abstract Europe Pmc



Http Cais Uga Edu Wp Content Uploads 19 01 Xrf Background Pdf



Validity Of Valence Estimation Of Dopants In Glasses Using Xanes Analysis Scientific Reports



Www Ssrl Slac Stanford Edu George Pickup Exafs 12 Pdf



Www Osti Gov Servlets Purl



The Physics And Technology Of Mammography




Ka And Bremsstrahlung X Ray Radiation Backlighter Sources From Short Pulse Laser Driven Silver Targets As A Function Of Laser Pre Pulse Energy Physics Of Plasmas Vol 21 No 3




Epos Trade




Mammography Lin Major Reference Works Wiley Online Library



X Ray Production Emission And Filtration




Basic Physics Of Digital Radiography The Patient Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



Exafs Spectroscopy As A Tool To Probe Metal Support Interaction And Surface Molecular Structures In Oxide Supported Catalysts Application To Al 2 O Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 B2969d
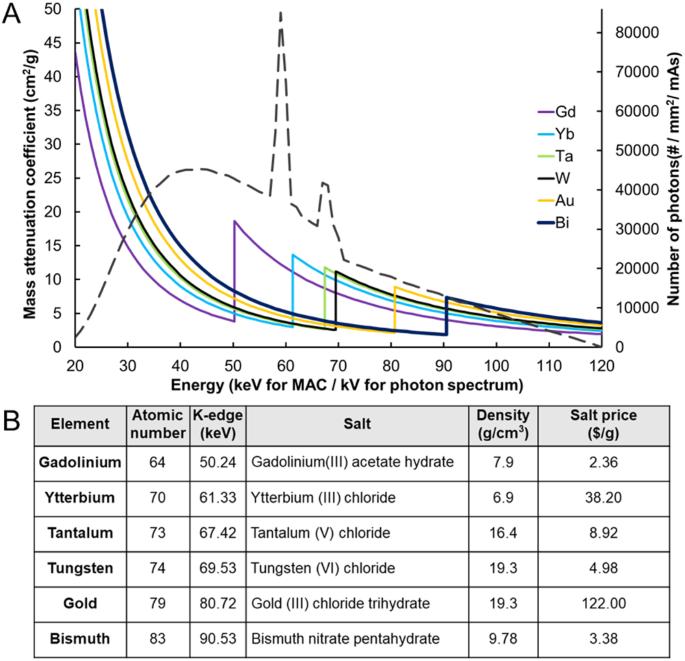



Assessment Of Candidate Elements For Development Of Spectral Photon Counting Ct Specific Contrast Agents Scientific Reports




First Demonstration Of 10 Kev Width Energy Discrimination K Edge Radiography Using A Cadmium Telluride X Ray Camera With A Tungsten Target Tube Sciencedirect




K Edge Subtraction Synchrotron X Ray Imaging In Bio Medical Research Physica Medica European Journal Of Medical Physics



Http Bib Pubdb1 Desy De Record Files Jonane Cumoo4 Revised Pdf



X Ray Machine



Arxiv Org Pdf 1404 2612




Cdte Measurement Of X Ray Tube Spectra Escape Events Amptek X Ray Detectors And Electronics




Radiation Quality Flashcards Quizlet




X Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Systematics At The Tungsten L Edge Inorganic Chemistry



Pure Mpg De Rest Items Item Component File Content



1




In Situ Vanadium K Edge And Tungsten Liii Edge X Ray Absorption




X Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Systematics At The Tungsten L Edge Inorganic Chemistry




Photon Counting X Ray Detectors For Ct Iopscience




Sulfur K Edge Micro And Full Field Xanes Identify Marker For Preparation Method Of Ultramarine Pigment From Lapis Lazuli In Historical Paints Science Advances




Esr 2 Highz Sensor Materials On Medipix 3




Pdf Study Of The Electronic Structure Of Rhenium And Tungsten Oxides On The O K Edge Juris Purans Academia Edu



1
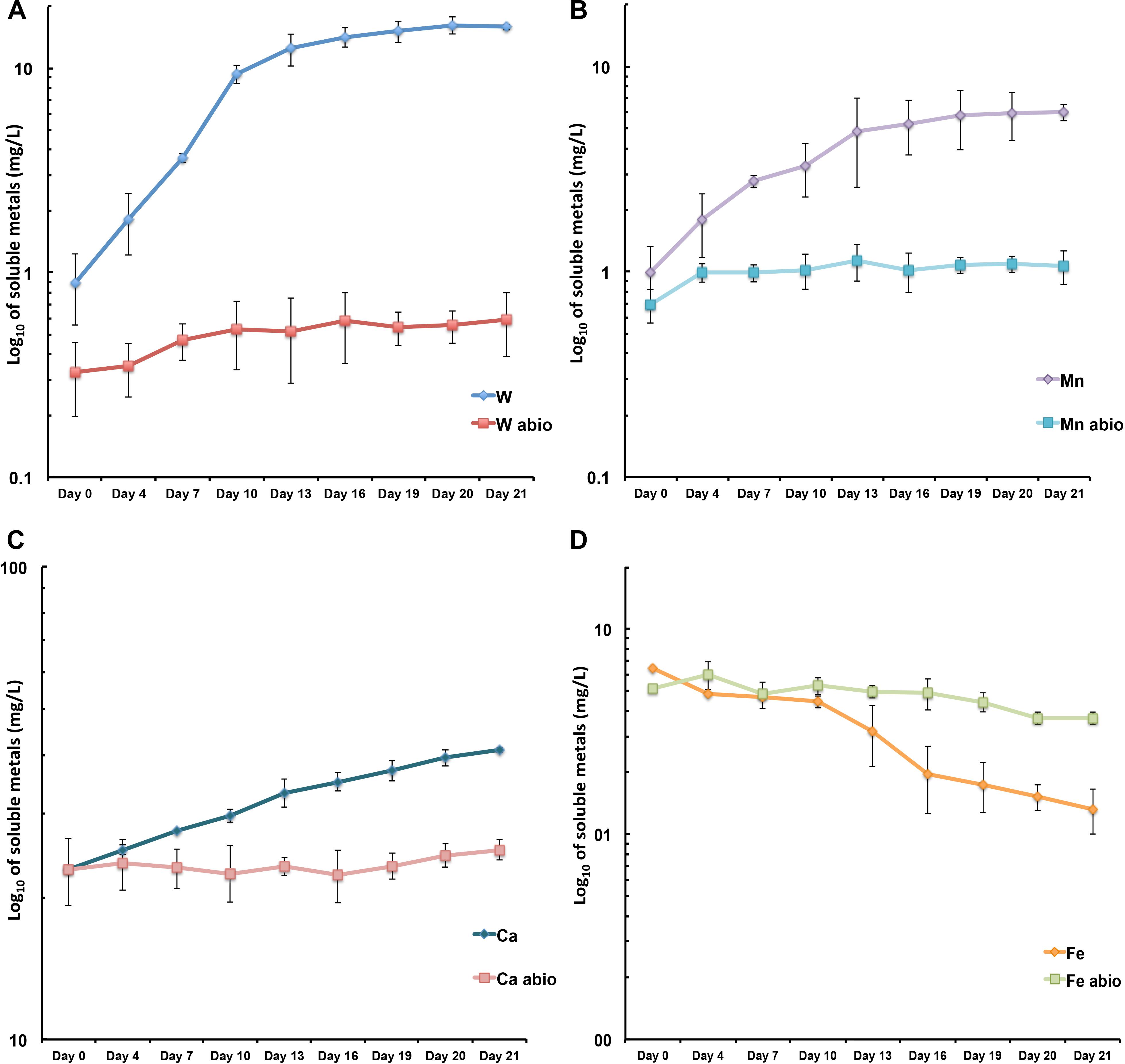



Frontiers Biotransformation Of Scheelite Cawo4 By The Extreme Thermoacidophile Metallosphaera Sedula Tungsten Microbial Interface Microbiology




Screen Film Radiography Frcr Physics Notes




X Ray Absorption Only At Single K Edge Physics Stack Exchange




15 Mcps Photon Counting X Ray Computed Tomography System Using A Zno Mppc Detector And Its Application To Gadolinium Imaging Sciencedirect



1




X Ray Absorption Only At Single K Edge Physics Stack Exchange
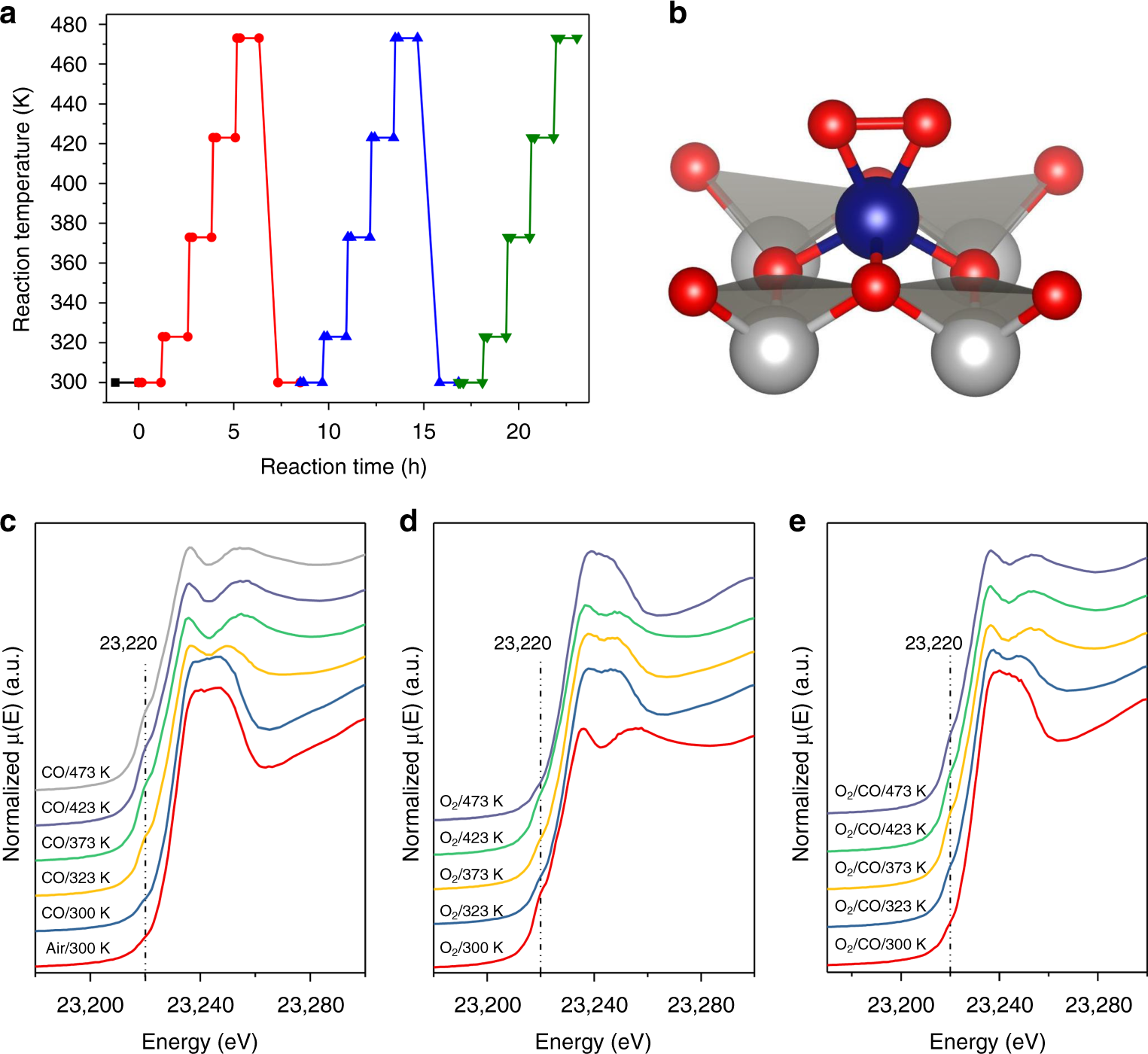



In Situ Spectroscopy Guided Engineering Of Rhodium Single Atom Catalysts For Co Oxidation Nature Communications




Cdte Measurement Of X Ray Tube Spectra Escape Events Amptek X Ray Detectors And Electronics
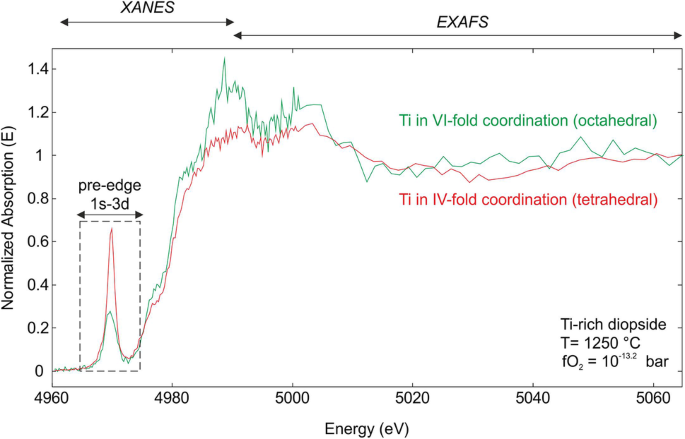



Ti K Edge Xanes Study On The Coordination Number And Oxidation State Of Titanium In Pyroxene Olivine Armalcolite Ilmenite And Silicate Glass During Mare Basalt Petrogenesis Springerlink



Www Mdpi Com 1996 1944 11 2 4 Pdf



Frcr Physics Lectures Diagnostic Radiology Ppt Video Online Download



Osa Towards Poisson Noise Limited Optical Pump Soft X Ray Probe Nexafs Spectroscopy Using A Laser Produced Plasma Source




Simultaneous X Ray Fluorescence And K Edge Ct Imaging With Photon Counting Detectors
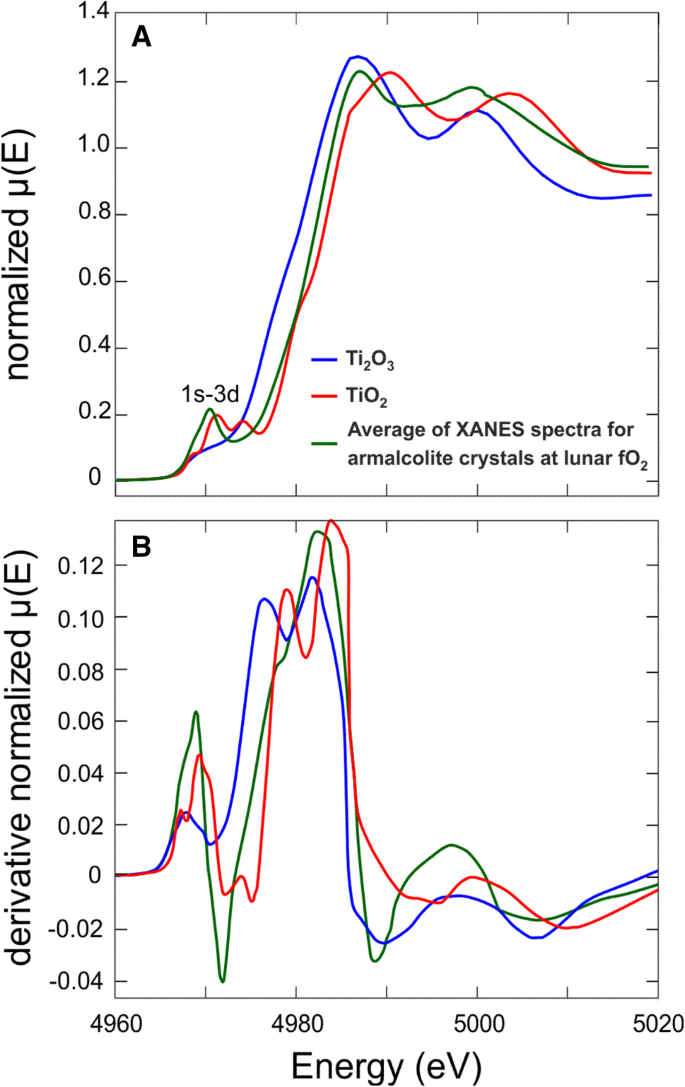



Ti K Edge Xanes Study On The Coordination Number And Oxidation State Of Titanium In Pyroxene Olivine Armalcolite Ilmenite And Silicate Glass During Mare Basalt Petrogenesis Springerlink




Figure 2 From Single Atom Tungsten Doped Ultrathin A Ni Oh 2 For Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation Semantic Scholar



Http Bib Pubdb1 Desy De Record Files Jonane Cumoo4 Revised Pdf




X Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Systematics At The Tungsten L Edge Inorganic Chemistry
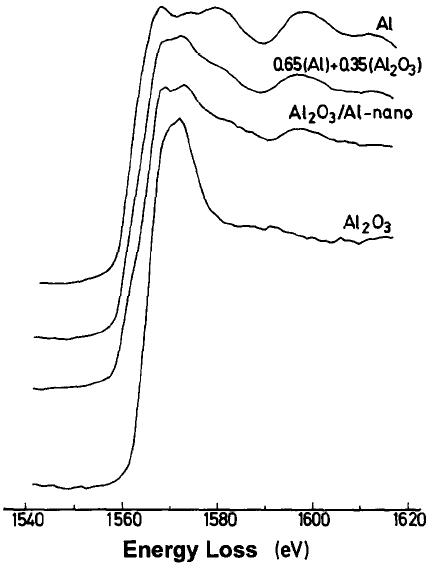



Eels Measurement Of Aluminum Al
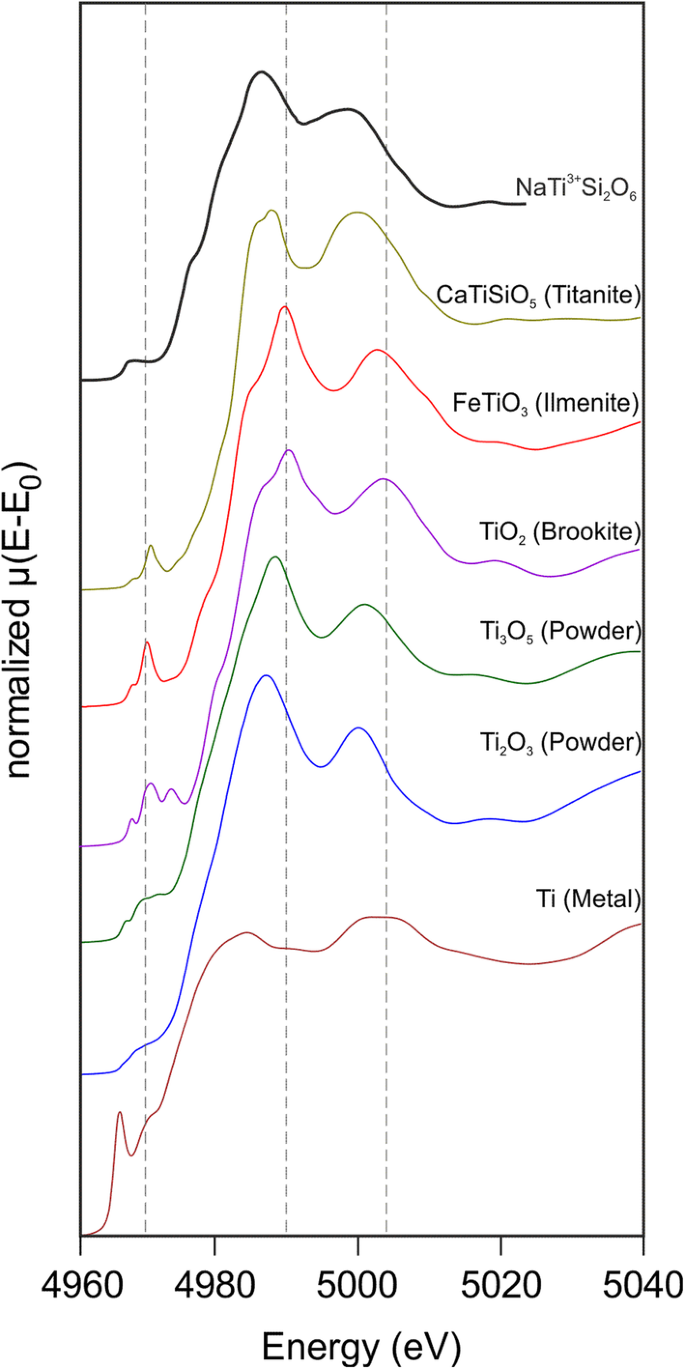



Ti K Edge Xanes Study On The Coordination Number And Oxidation State Of Titanium In Pyroxene Olivine Armalcolite Ilmenite And Silicate Glass During Mare Basalt Petrogenesis Springerlink




The K Absorption Edge Of An Unknown Element Is 0 171 A A Identify The Element B Find The Average Wavelengths Of The K Alpha K Beta And K Gama Lines C If A



X Ray Emission Spectroscopy Wikipedia
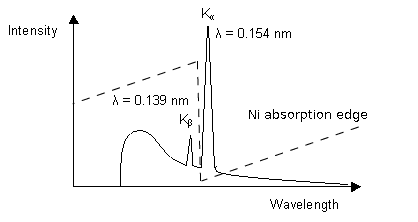



Doitpoms Tlp Library X Ray Diffraction Techniques Experimental Matters
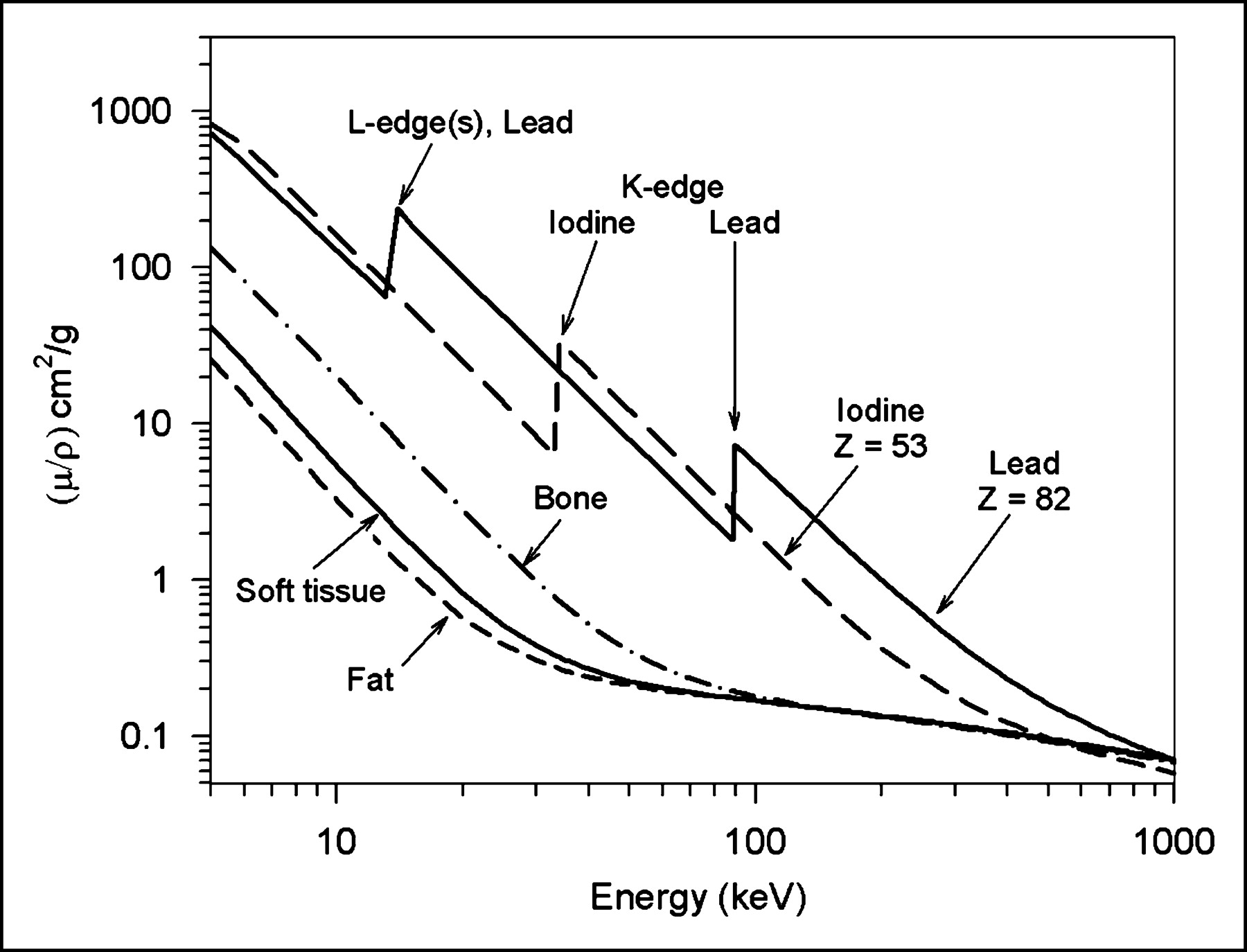



X Ray Imaging Physics For Nuclear Medicine Technologists Part 2 X Ray Interactions And Image Formation Journal Of Nuclear Medicine Technology
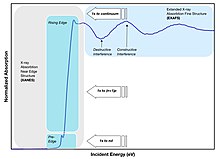



X Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Wikipedia



X Ray Physics X Ray Interaction With Matter X Ray Contrast And Dose Xrayphysics



Http Www Nims Go Jp Edge17 Olk Ultram Pdf



Escholarship Org Content Qt9rd0c0vg Qt9rd0c0vg Nosplash 181d121fdd5a8fffeea5b6e Pdf
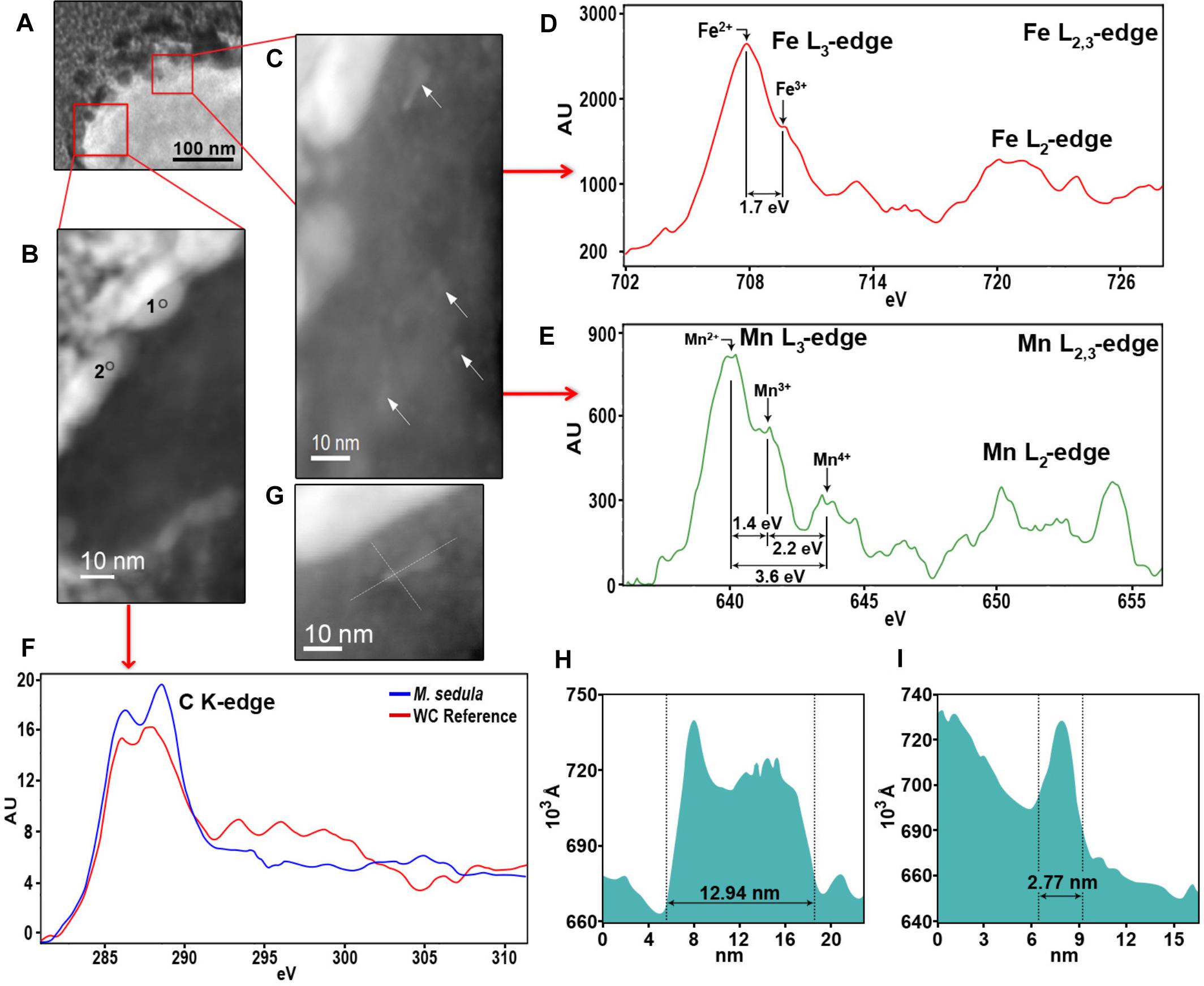



Frontiers Biotransformation Of Scheelite Cawo4 By The Extreme Thermoacidophile Metallosphaera Sedula Tungsten Microbial Interface Microbiology




Sulfur K Edge Micro And Full Field Xanes Identify Marker For Preparation Method Of Ultramarine Pigment From Lapis Lazuli In Historical Paints Science Advances




Sulfur K Edge Xas Of Wvo Vs Movo Bis Dithiolene Complexes Contributions Of Relativistic Effects To Electronic Structure And Reactivity Of Tungsten Enzymes Abstract Europe Pmc



The Physics And Technology Of Mammography




Frcr Physics Lectures Diagnostic Radiology Ppt Video Online Download



Web Stanford Edu Group Glam Xlab Matsci162 172 Lecturenotes 01 Properties safety Pdf



The Physics And Technology Of Mammography




Pdf Contrast Enhancement In Mammography Imaging Including K Edge Filtering Semantic Scholar



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿